Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4), also known as CD152, is a key regulator of T-cell immunity by maintaining activation and inhibition of T-cell immune responses. CTLA4 and CD28 are co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory cell surface signaling proteins that interact with the same ligands (CD80 and CD86), with CTLA4 displaying a greater affinity than CD28 for both, thus creating effective ligand binding competition. Studies have shown that functional blockage of CTL4 by anti-CTL4 binding by biologics and small molecules with high affinity results in enhanced T cell responses, ultimately resulting in more effective immune responses targeting many cancers.
To provide a screening assay for identifying small and large molecule CTLA-4 and CD80 binding interaction blockage inhibitors, with the goal of eventually studying immune responses to aid in the discovery of novel immunotherapies to combat cancer.
CTLA4-CD80
CTLA4: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4, CD152
CD80: T-lymphocyte activation antigen CD80, Activation B7-1 antigen, BB1, CTLA-4 counter-receptor B7.1 (B7)
HTRF Assay
Human CTLA4, human CD80
| Compounds | IC50 (nM) |
|---|---|
| Ipilimumab | 1.55 |
Malvern, PA, USA
More information can be found on our website Immune Checkpoint Assays
Reference compound inhibition of CTLA4-CD80
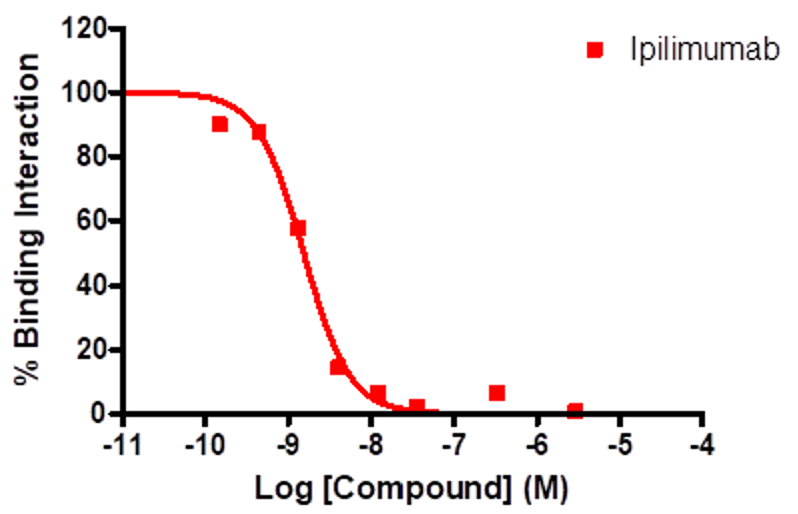
Sample data showing reference compound inhibition of CTLA4-CD80 binding interaction