T Cell Assays
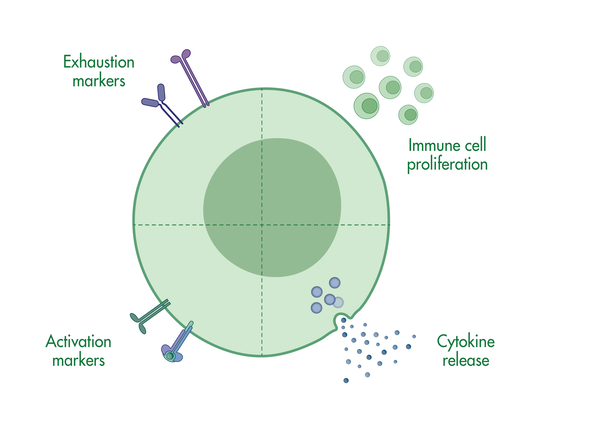
Our T cell assays are designed to characterize T cells via T cell proliferation assays, T cell activation assays, and T cell cytotoxicity assays, or monitoring T cell differentiation via immune markers.
T cells reside in peripheral tissue or circulate in the body until they recognize their antigen on the surface of an antigen-presenting cell. The interaction with the antigen-presenting cell sets a complex response in motion. Our T cell assays are designed to understand which signals trigger a response and to characterize this response.
T cell assays at Reaction Biology include:
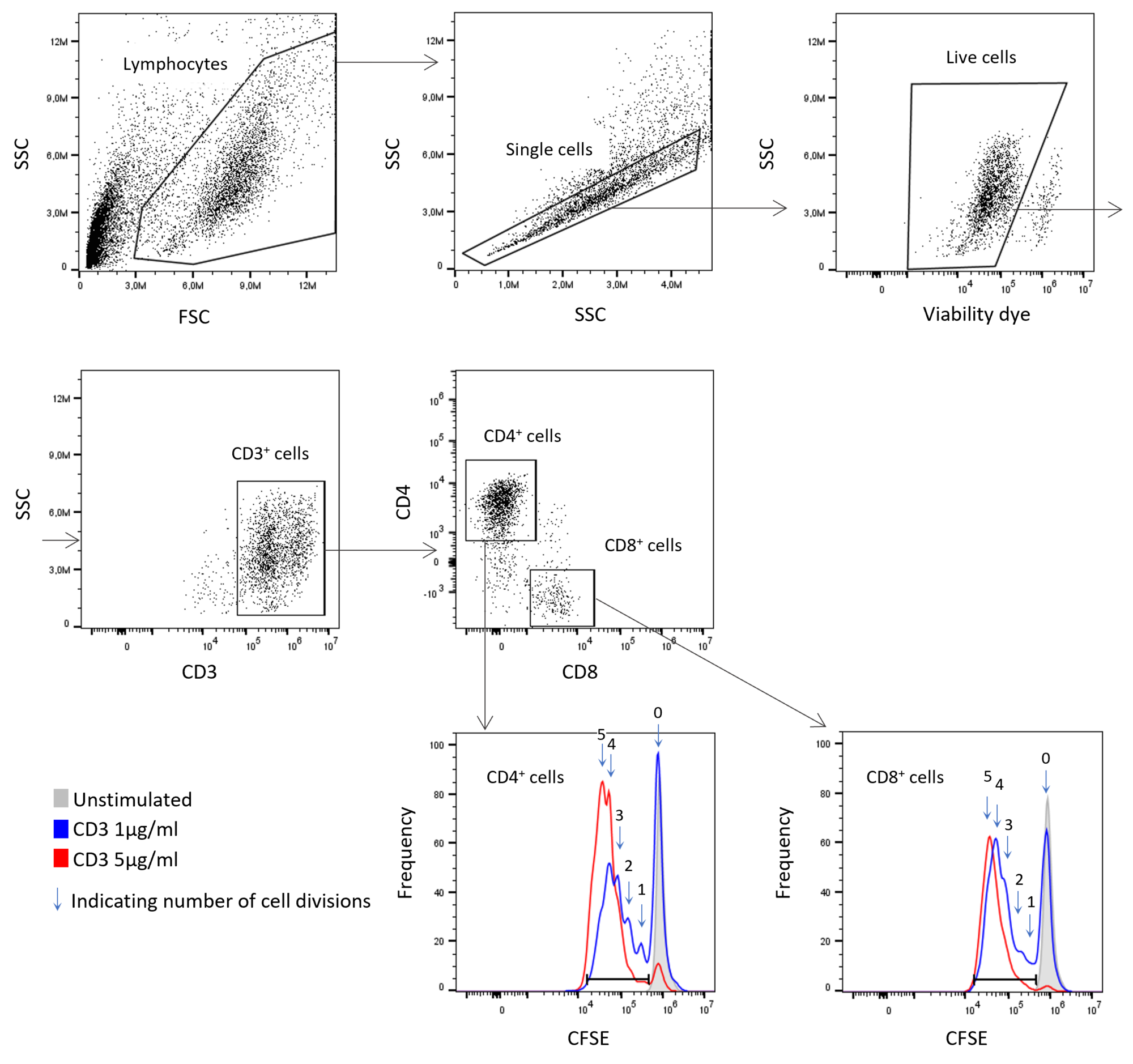
- T cell proliferation assays to monitor the expansion of T cells after activation
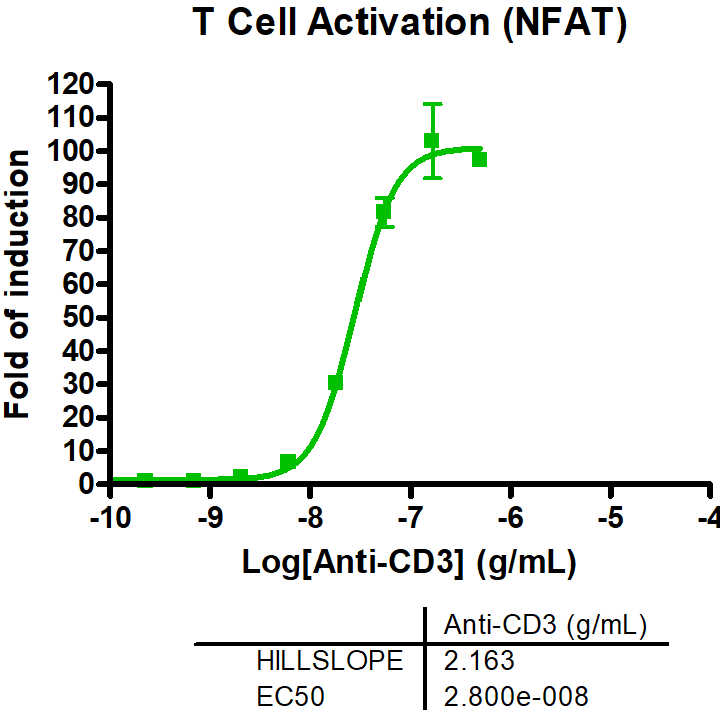
- T cell activation assays to monitor hallmarks for T cell activation, including cytokine release and immune surface markers
- T cell cytotoxicity assays measuring the number of cytokine-secreting cells via ELISpot
Please reach out today and discuss directly with our scientists how we can help you best to characterize your new immunotherapeutic agent.