Soft Agar Assay (Colony Formation Assay)
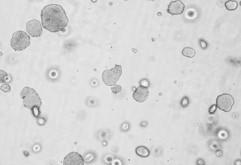
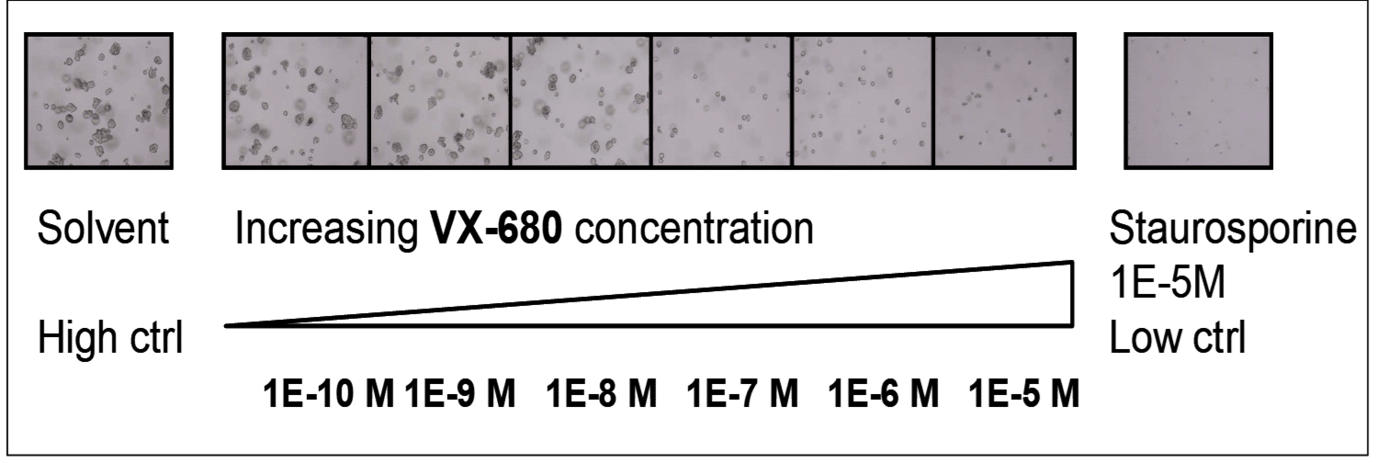
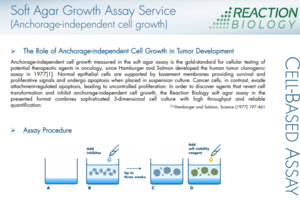
The Colony Formation Assay, also called a clonogenic assay, allows screening of the therapeutic efficacy of drugs for anchorage-independent cell growth floating in soft agar. In the Soft Agar Assay, cells grow from single cells to cell colonies in an agar solution keeping them from the solid surface and allows growth in an anchorage-independent way.
The anchorage-independent formation of cell colonies is one of the hallmark characteristics of cellular transformation and uncontrolled cell growth. Normal epithelial cells are supported by basement membranes providing survival and proliferative signals and undergo apoptosis when placed in suspension culture. Tumor cells, in contrast, evade attachment-regulated apoptosis, leading to uncontrolled proliferation. In order to discover agents that revert cell transformation and inhibit anchorage-independent cell growth, the Soft Agar Assay combines sophisticated 3D cell culture with a high throughput setup and reliable quantification.
What is a Soft Agar Assay?
The Soft Agar Assay is one of two 3D assays offered by Reaction Biology. The Soft Agar Assay is used to test the impact of drugs on the proliferation of single cells growing into colonies. In contrast, the 3D Tumor Spheroid Assay is used for testing a drug’s anti-proliferative and cytotoxic capacity on existing tumor spheroids.
Our colony formation assay service provides the following benefits:
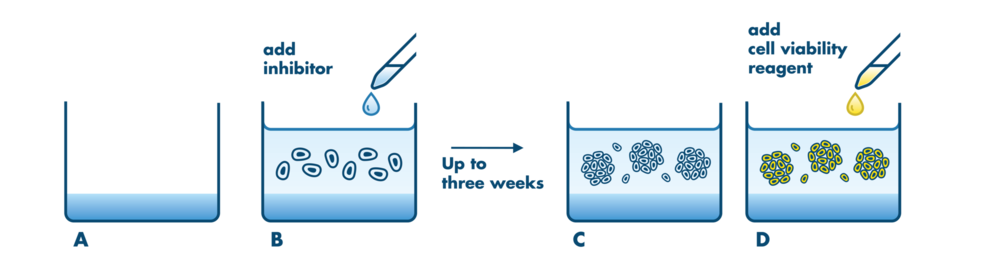
- Longterm exposure: Up to three weeks of compound exposure possible
- Available for drug combination treatment
- All cell lines are subject to authentification via STR profiling