Protein Detection Methods
At Reaction Biology, protein detection supports biomarker discovery, monitoring of pharmacodynamic markers, and MoA analysis.
We offer three methods for protein analysis:
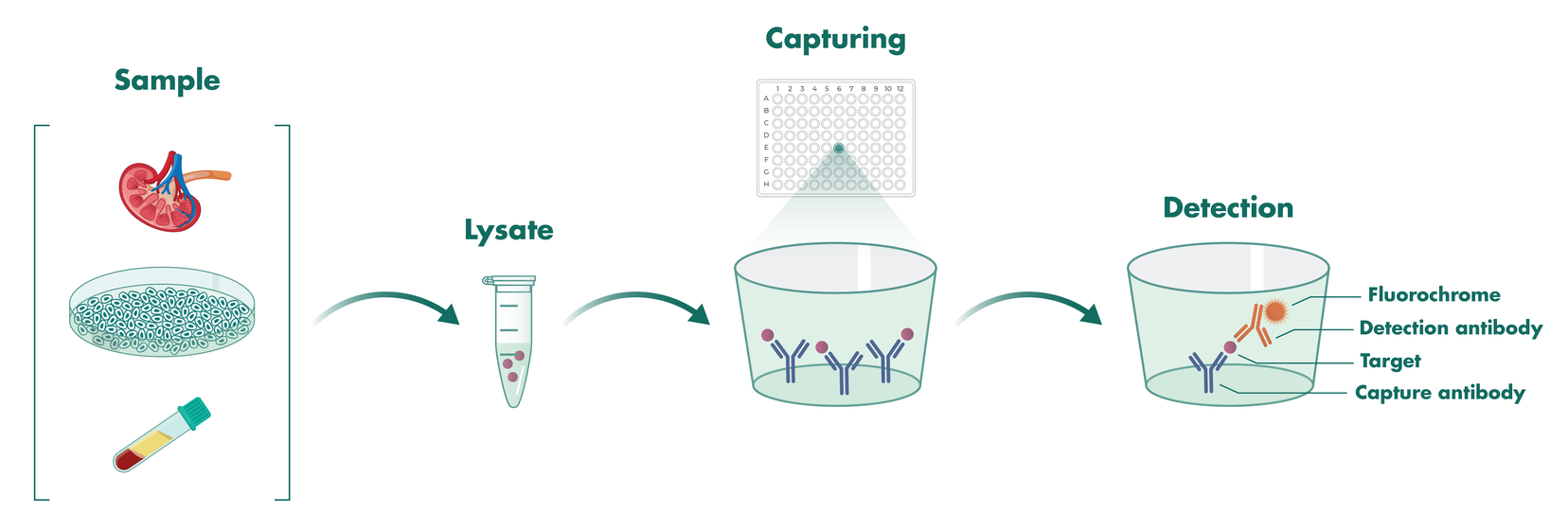
- ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is a high-throughput method to quantify proteins in cells or other biological samples, including liquids. The protein of interest is detected with specific antibodies and quantified with high accuracy.
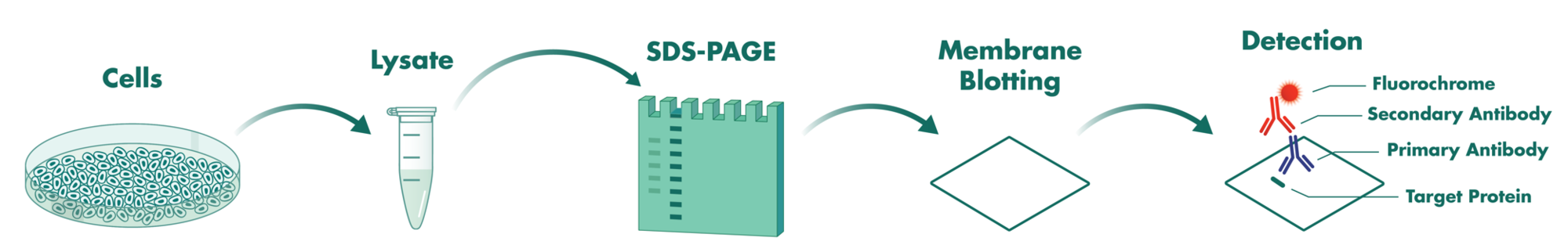
- Western Blot Services enable the detection of proteins in biological samples based on specific antibodies and the molecular size of the protein. Our Western Blot Service provides qualitative and quantitative means to investigate the modulation of protein expression or post-translational modifications.
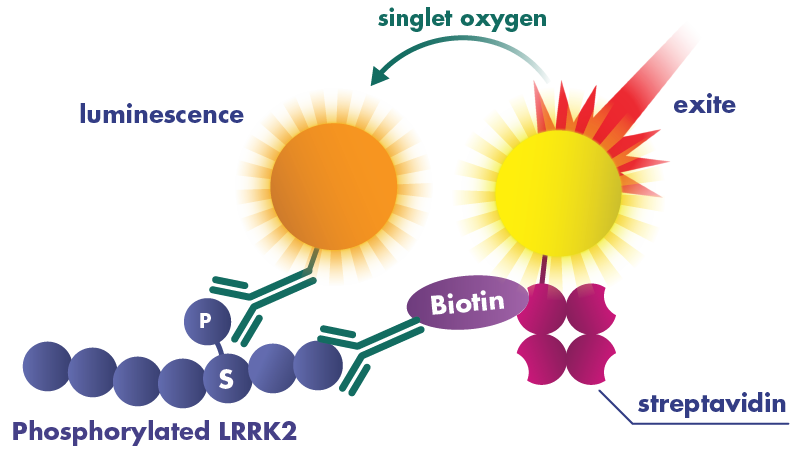
- Alpha technology comprises AlphaLISA and AlphaScreen, which are homogenous assay formats for the detection of protein-protein interactions or protein modifications such as phosphorylation. The Alpha technology is a highly sensitive method enabling high-throughput screening with no wash steps guaranteeing reproducible results. The assay requires two antibodies that specifically bind to the protein of interest.
In addition, we also offer multiplexing methods for protein science including multiplex ELISA via Meso Scale Discovery technolgy and flow cytometry.
In most cases, our protein detection methods can be custom-tailored to the client’s specific needs. Connect with our scientific team to find out how we can best support your research goals.