In Vitro Angiogenesis Assay for Drug Testing
The Angiogenesis Assay allows for the evaluation of pro- or anti-angiogenic effects of drugs on HUVEC sprouting capacity on a cellular basis.
Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, is a physiological process during growth and development. Beyond that, angiogenesis is necessary for tumor growth and is involved in other pathological disorders (e.g. psoriasis, macular degeneration).
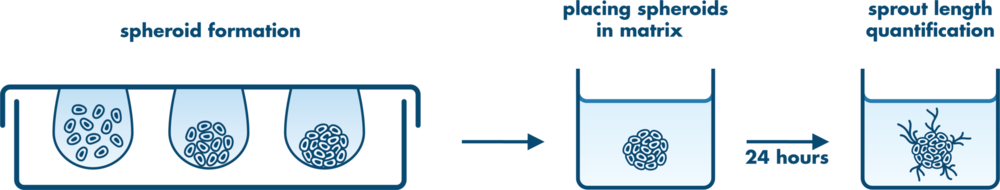
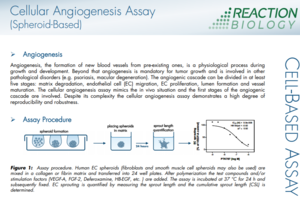
The In Vitro Angiogenesis Assay is a vessel sprouting assay that mimics the in vivo situation with respect to the first stages of the angiogenic cascade, (i) the sprouting in a 3D environment promotes cell-cell signaling between the endothelial cells, (ii) the surrounding matrix is degraded before the invasion, (iii) the spheroids used in the angiogenesis assay generate sprouts that are close to the physiological arrangement of endothelial cell vessels
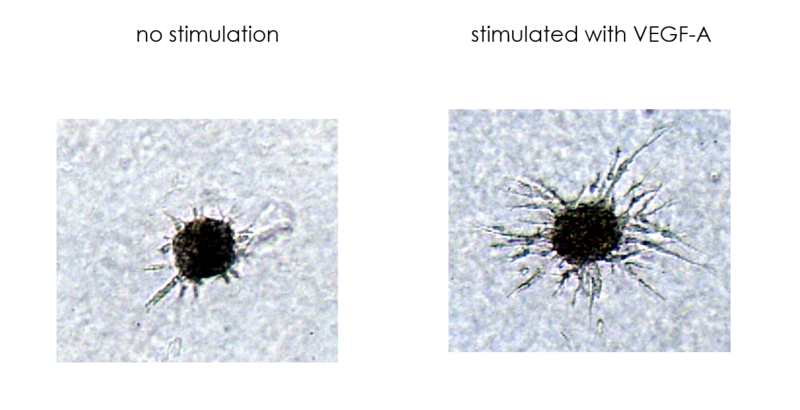
- Vessel sprouting can be induced by VEGF-A, FGF-1, FGF-2, DFO, or others
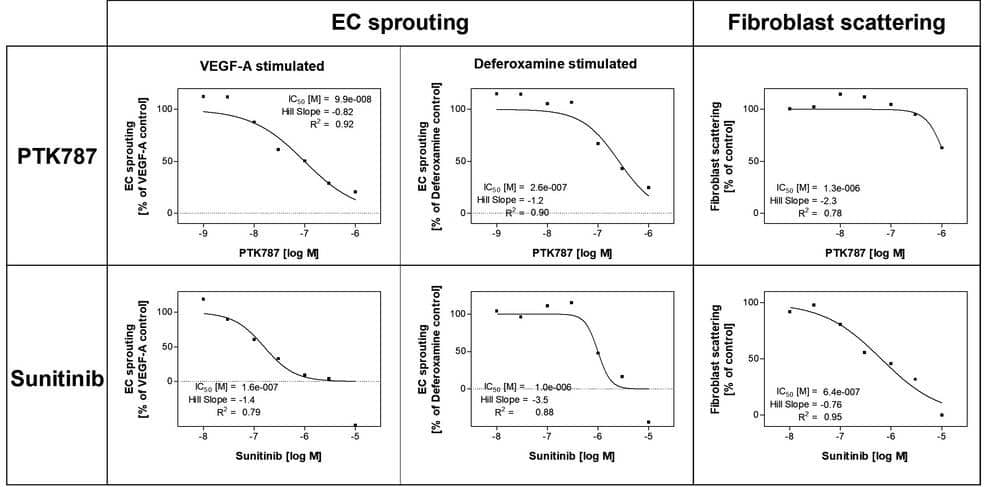
- IC50 determination can be performed for angio-stimulating and angio-inhibiting compounds
- The in vitro angiogenesis assay is reproducible and robust despite its complexity