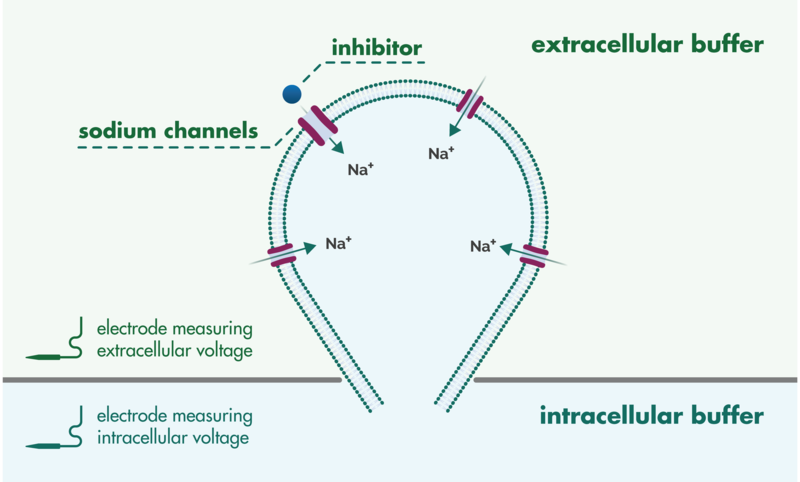
Patch Clamp Assay Services
Our fully automated patch clamp platform comprises QPatch HTX and QPatch 16 that allows for the testing of up to 48 or 16 cells in parallel, respectively.
QPatch are medium-throughput machines suitable for confirming hits from larger screens and also for lead optimization. QPatch offers high-quality measurements with the formation of gigaohm seals. The platform can be used to assay both voltage-gated and ligand-gated channels and utilizes stable cell lines.
- Compound profiling against the Cardiac Safety Panel including hERG, Nav1.5, and Cav1.2
- Positive control and vehicle control in every assay
- Single concentration profiling and full concentration-response curves

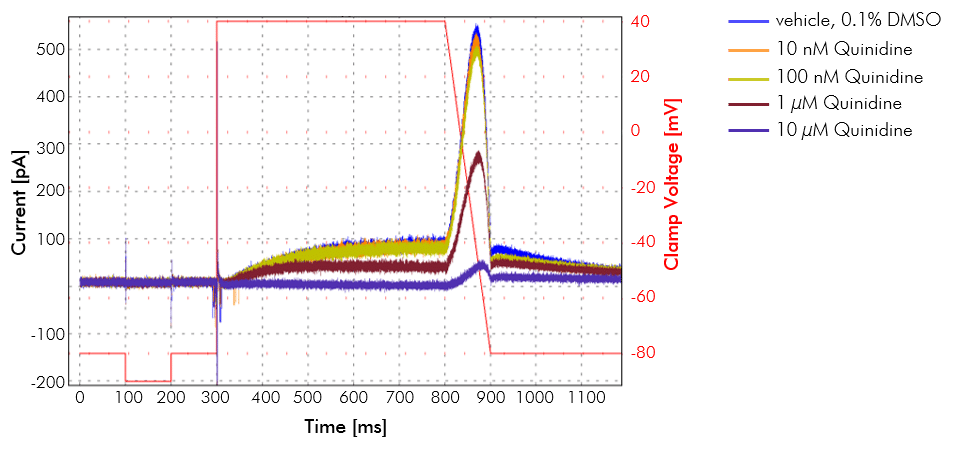
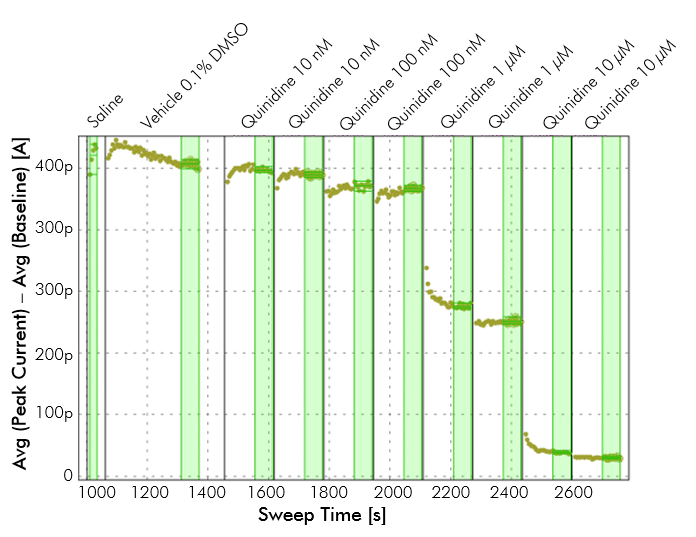
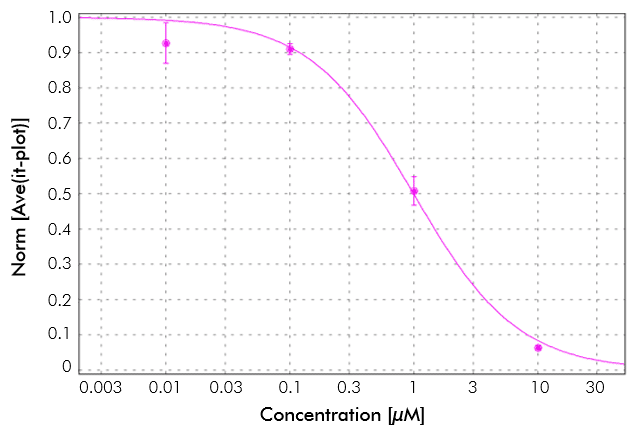
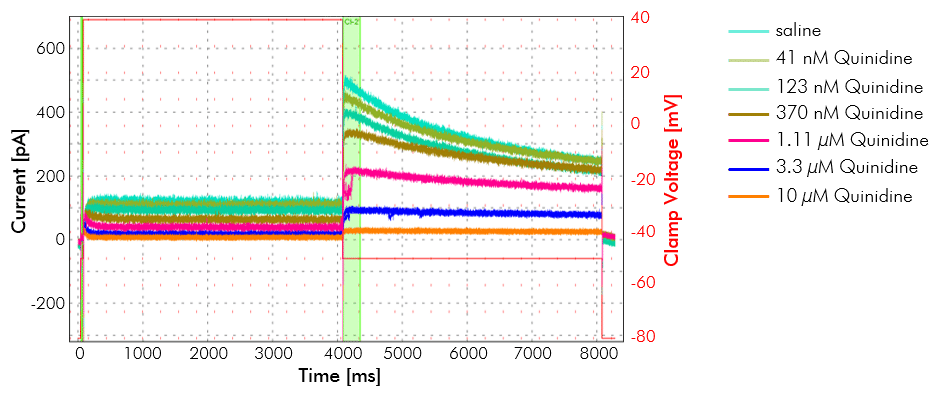 Example of hERG inhibition. hERG potassium channel inhibition in the presence of various concentrations of an antiarrhythmic agent. Recordings were made on the IonFlux in CHO cells stably expressing hERG voltage-dependent potassium channel. Each concentration of the drug was perfused for 5 minutes. A drug concentration of 10 µM shows close to complete inhibition of hERG.
Example of hERG inhibition. hERG potassium channel inhibition in the presence of various concentrations of an antiarrhythmic agent. Recordings were made on the IonFlux in CHO cells stably expressing hERG voltage-dependent potassium channel. Each concentration of the drug was perfused for 5 minutes. A drug concentration of 10 µM shows close to complete inhibition of hERG.