Macrophage Cell-based Assays
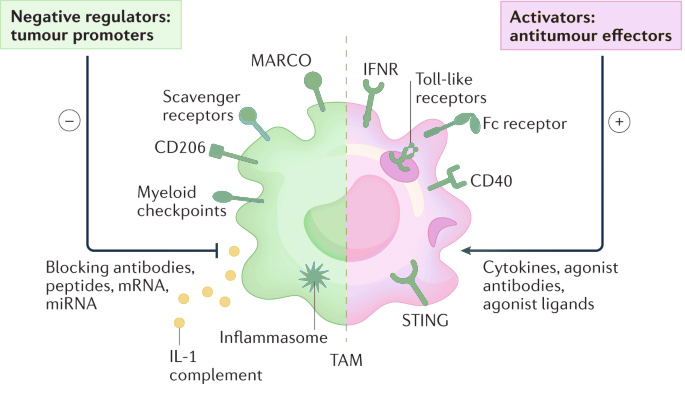
Macrophage cell-based assays are employed to assess macrophage function, focusing especially on their contribution to the tumour microenvironment. In the context of cancer, tumour-associated macrophages often develop an anti-inflammatory phenotype that supports cancer progression, making them a novel target for emerging immunotherapies. These assays provide an valuable tool for in vitro analysis of macrophage function by:
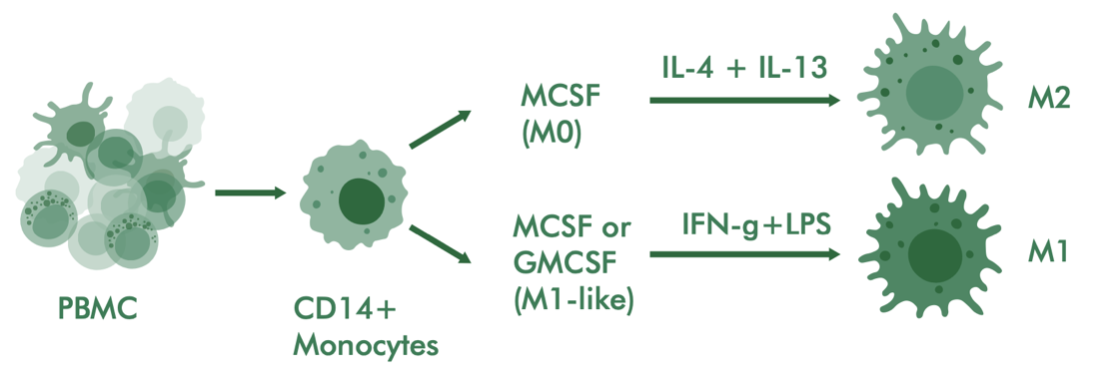
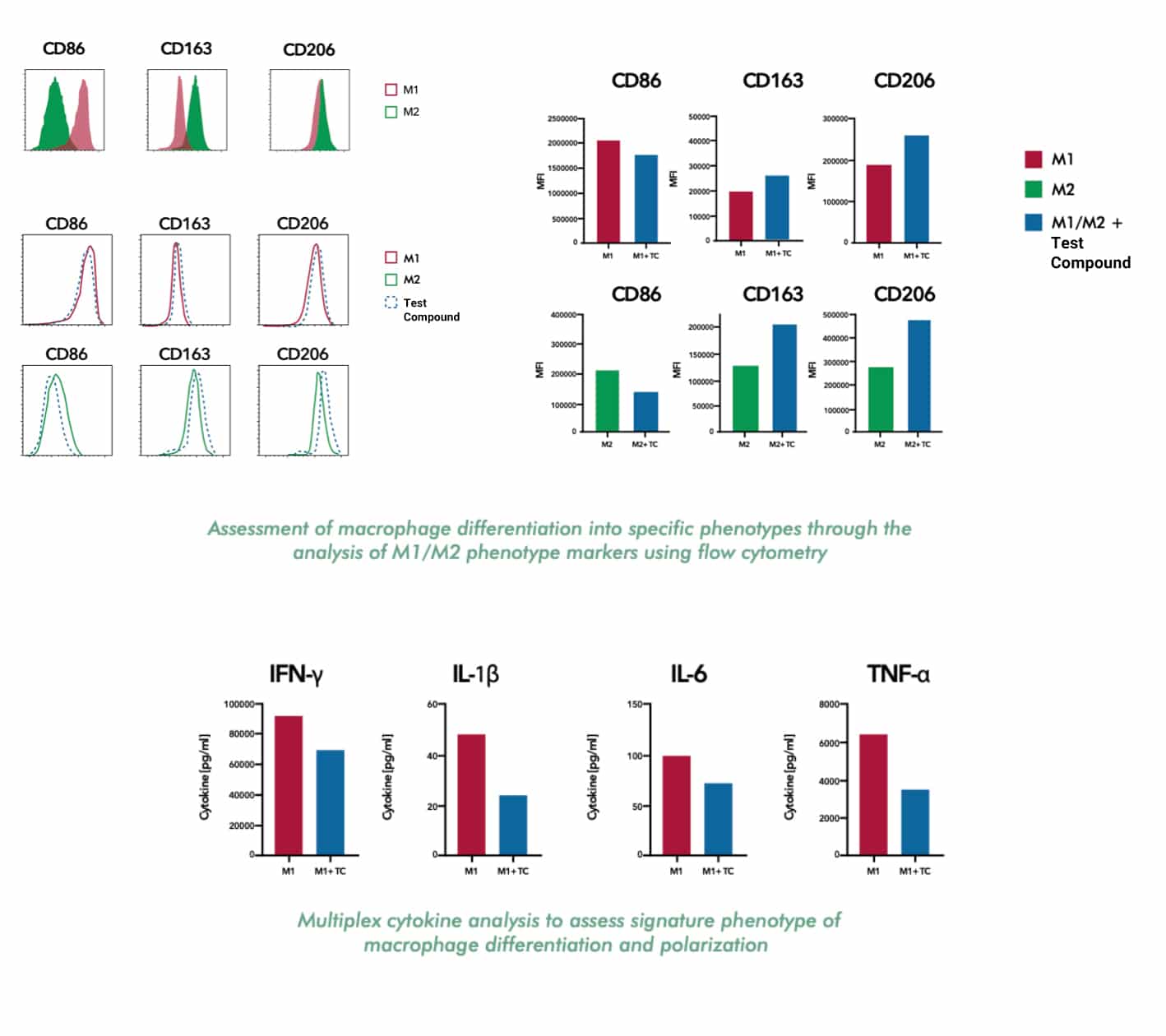
- Assessing macrophage polarization
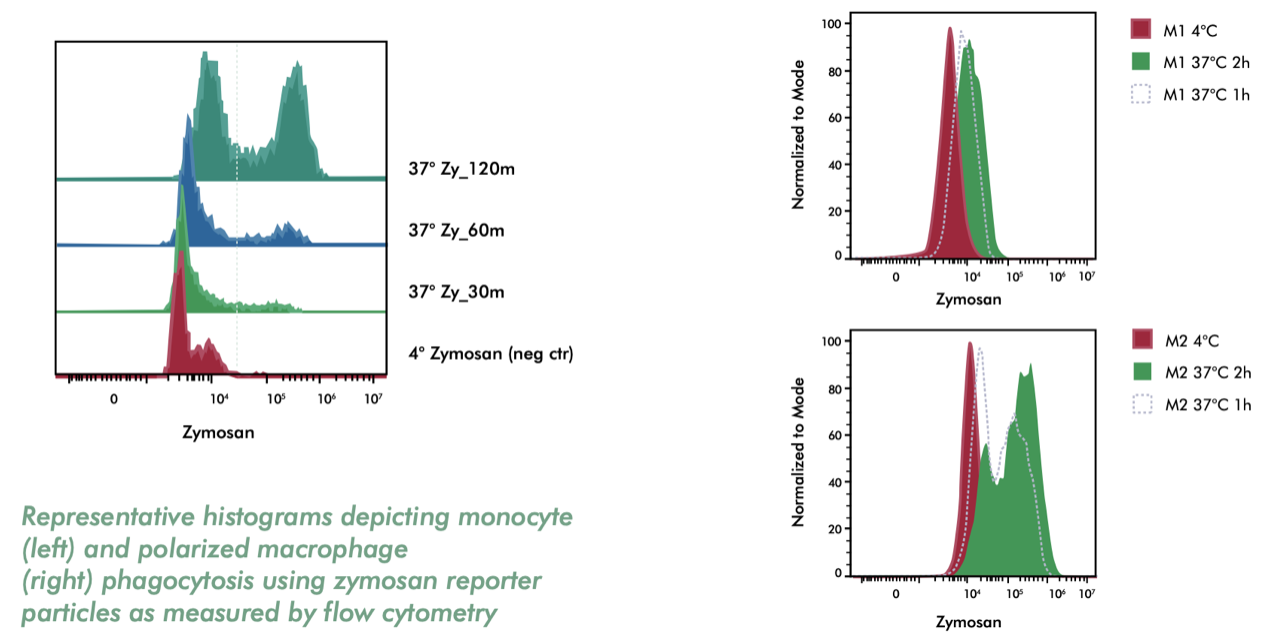
- Measuring macrophage phagocytosis
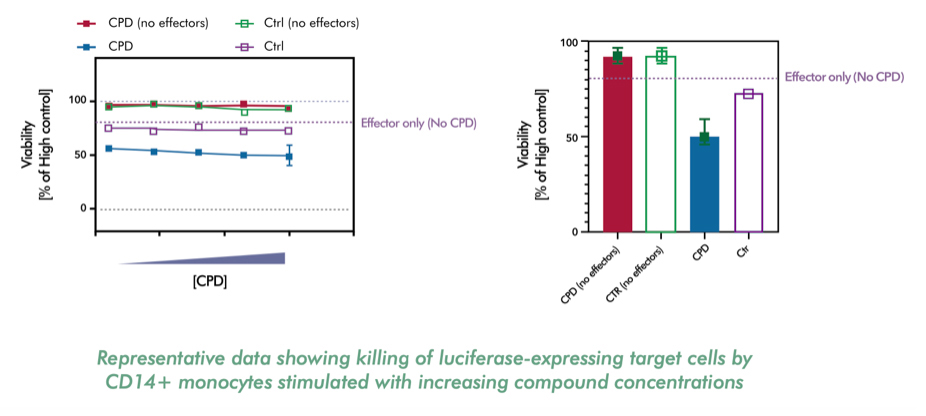
- Evaluating target cell killing and inflammatory cytokines release by activated monocytes
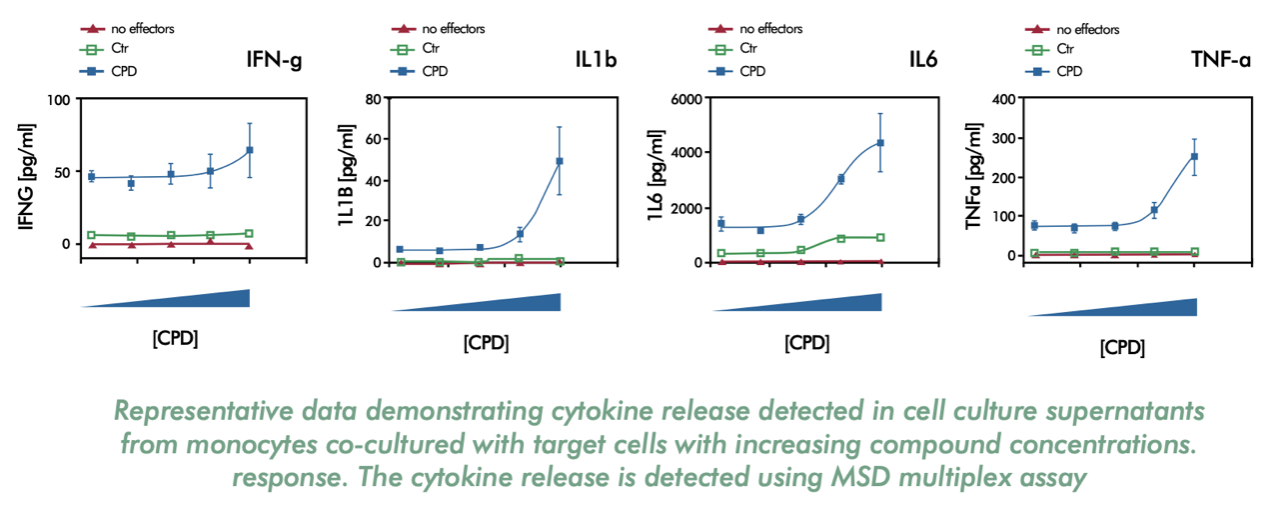
- Analysing the secretion of cytokines
Our suite of four macrophage cell-based assays offers a robust platform for evaluating the impact of your next generation immunotherapeutics on macrophage or monocyte function.