Cell-based Epigenetic Assays
Cell-based epigenetic assays are valuable to probe new drug candidates in the physiologic environment of intact cells. They are the natural second step after the initial screening of new compounds in biochemical assays adding valuable biologically relevant information for the efficacy of the compounds.
Reaction Biology offers three options for cellular epigenetic inhibitor testing:
1. Functional Assays: Testing the modulation of the histones including acetylation, methylation, and phosphorylation.
2. Binding Affinity: Using Promega’s NanoBRET technologies we can test the binding affinity and residence time of new epigenetic compounds in intact cells
3. Protein:Protein Interaction: Testing the interaction of bromodomains with histones in intact cells based on Promega’s NanoBRET Bromodomain/Histone Interaction Assay.

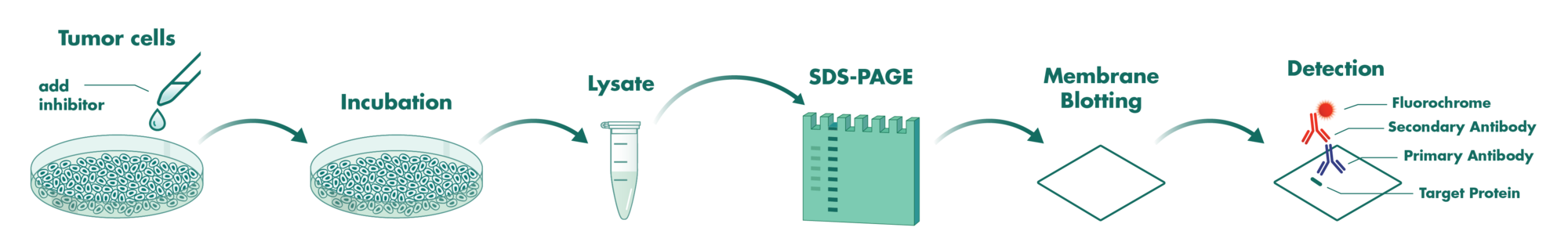
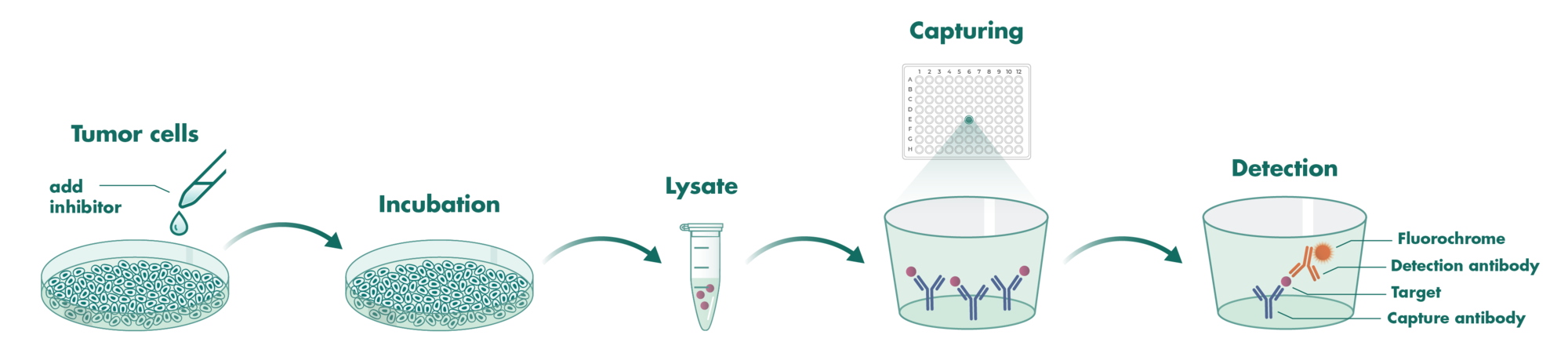
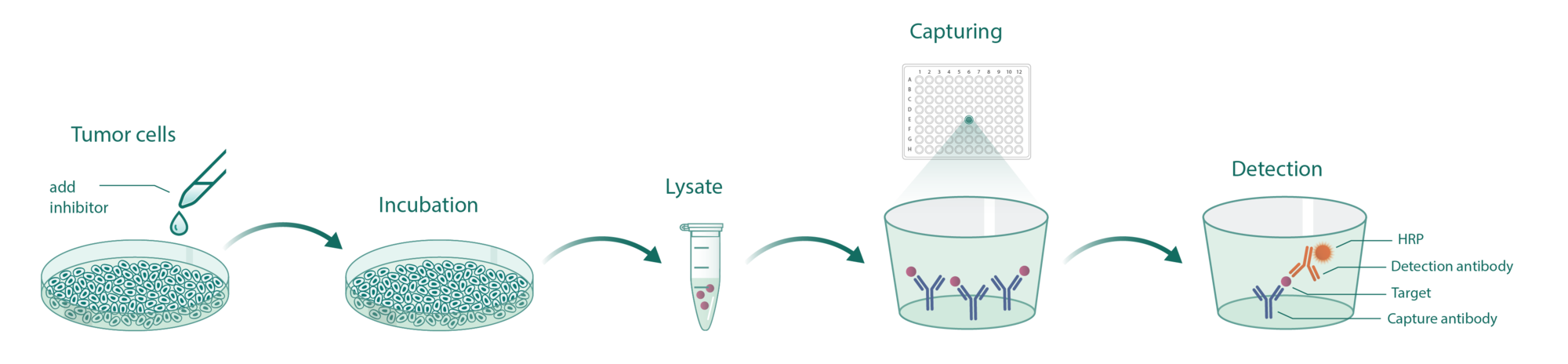
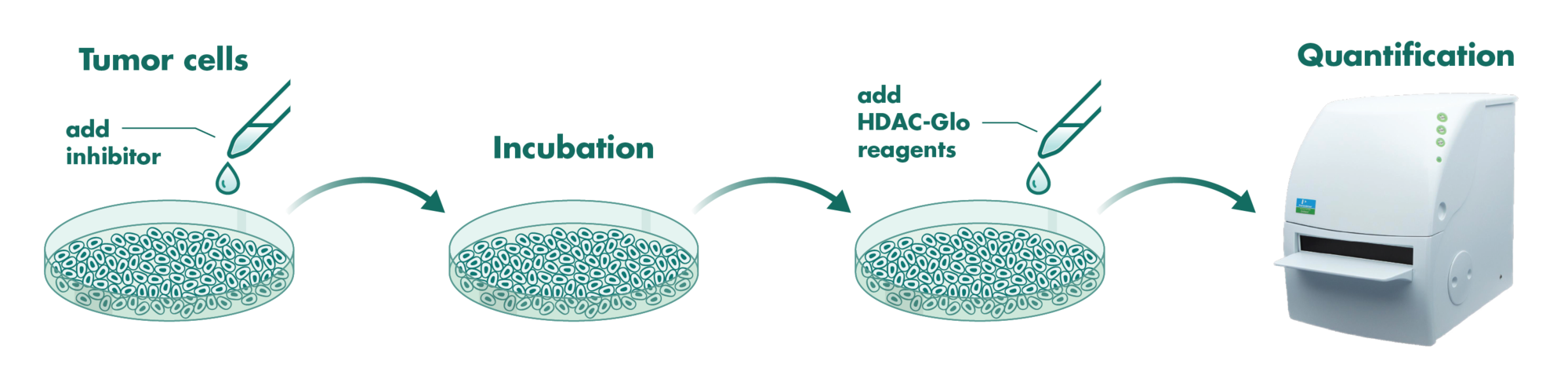 Cells incubate with the compound for 1 hour in serum-free medium. The HDAC-Glo substrate is added with is an acetylated peptide fused to aminoluciferin. After deacetylation of the peptide by HDAC activities, the peptide is cleaved via a protease in the reagent to release aminoluciferin substrate which is quantified in a reaction using luciferase. The luminescence is quantified via an Envision 2104 Multilabel Reader.
Cells incubate with the compound for 1 hour in serum-free medium. The HDAC-Glo substrate is added with is an acetylated peptide fused to aminoluciferin. After deacetylation of the peptide by HDAC activities, the peptide is cleaved via a protease in the reagent to release aminoluciferin substrate which is quantified in a reaction using luciferase. The luminescence is quantified via an Envision 2104 Multilabel Reader.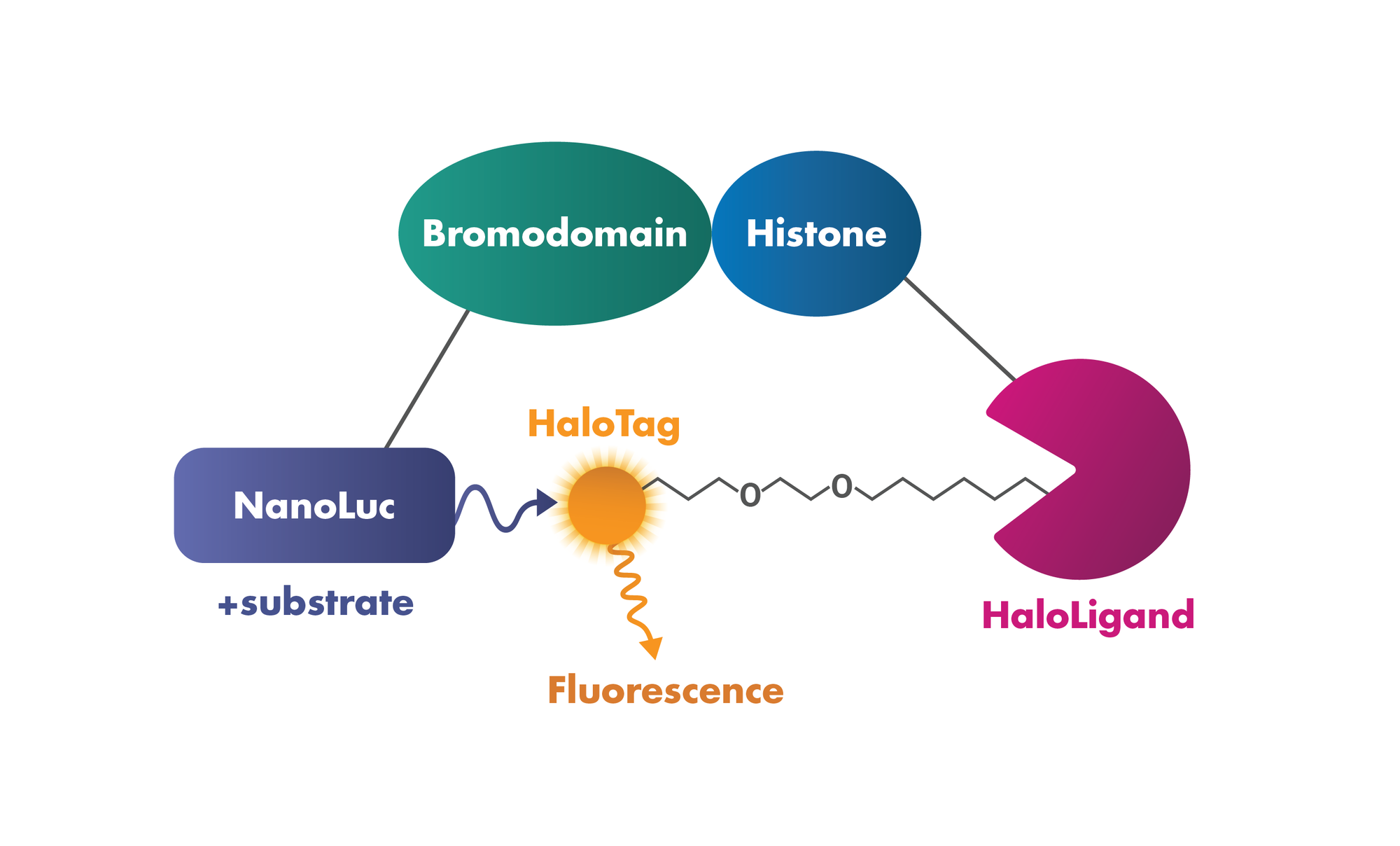
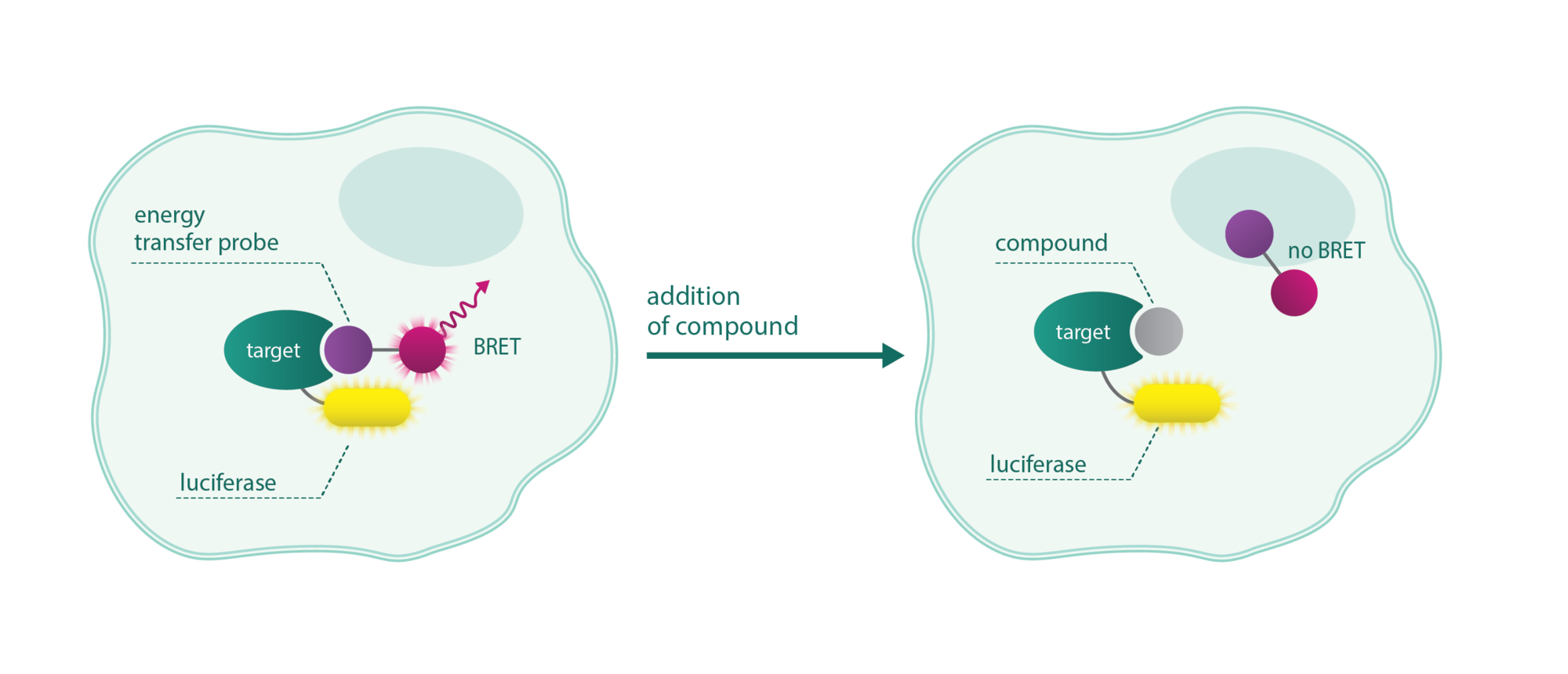 NanoBRET assays are compound competition assays that rely on bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) between a luciferase-tagged target and a fluorescent tracer. In the presence of the compound, the tracer is replaced diminishing the fluorescence.
NanoBRET assays are compound competition assays that rely on bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) between a luciferase-tagged target and a fluorescent tracer. In the presence of the compound, the tracer is replaced diminishing the fluorescence.

