Humanized Syngeneic Models
Humanized mouse models enable rapid testing of human target-specific immunotherapy drug candidates by providing genetically engineered human targets in a fully immunocompetent host.
Our humanized mouse models can help you understand your drug’s mechanisms of action, kinetics, toxicity profile, and potency, allowing you to select a drug candidate with the highest chance of success in the clinic.
Our team of experts have extensive knowledge in the field of preclinical modelling and long-standing expertise in assessing the efficacy and potency of immuno-oncology drug candidates using humanized mouse models.
What we offer:
- A panel of well-established models expressing clinically-relevant human targets (developed in collaboration with genOway)
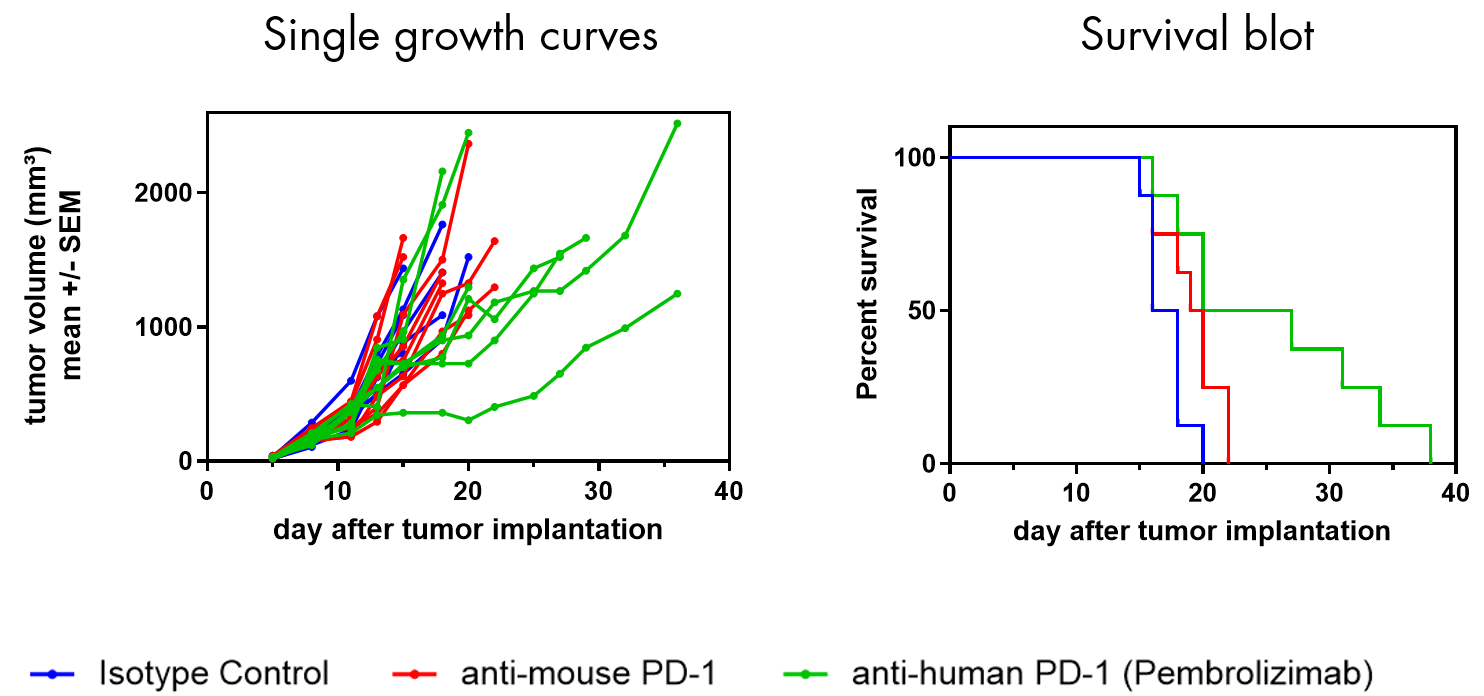
- Models suitable for response to human immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g. Pembrolizumab, Nivolumab, Ipilimumab) to evaluate combinations strategies with your test compound
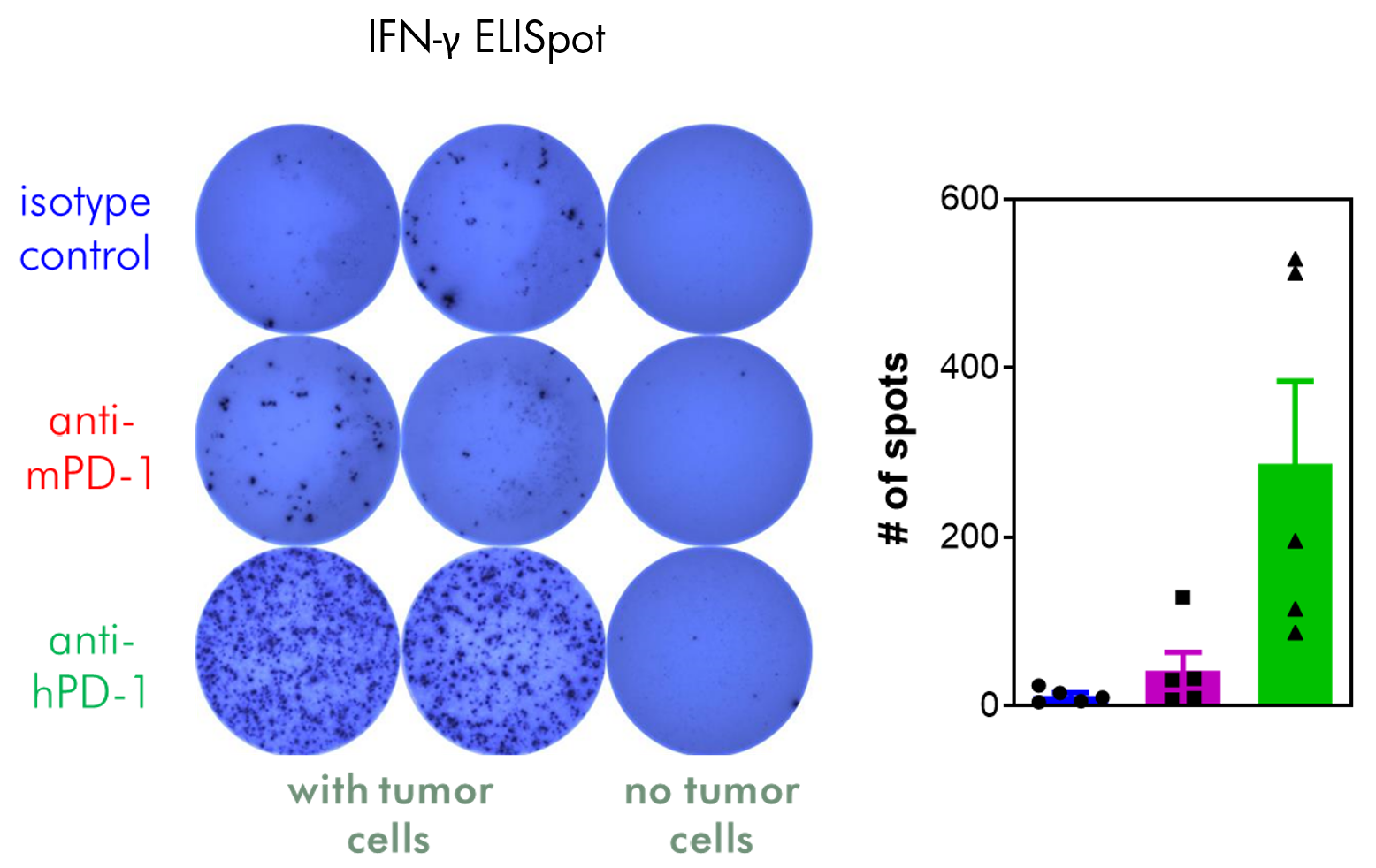
- Flow cytometry readout for immune cell profiling
- A team of expert immunologist available to guide your study design and support data analysis
Reach out today to discuss how we can fast-track your immunotherapy research.